The ROMAN CIVILIZATION
IMAGES OF THE ROMAN CIVILIZATION
THE ROMAN CULTURE
of the ancient Roman civilization
The Culture of the Romans thought of themselves as highly religious, and attributed their success as a world power to their collective piety in maintaining good relations with the gods. Most Roman towns and cities had a forum, temples and the same type of buildings, on a smaller scale, as found in Rome
Most early Roman painting styles show Etruscan influences, particularly in the practice of political painting. In the 3rd century BCE, Greek art taken as booty from wars became popular, and many Roman homes were decorated with landscapes by Greek artists. Evidence from the remains at Pompeii shows diverse influence from cultures spanning the Roman world
Architecture reflected elements of architectural styles of the Etruscans and the Greeks. Over a period of time, the style was modified in tune with their urban requirements, and the civil engineering and building construction. The Roman concrete has lasted more than two thousand years some of ancient Roman structures still stand magnificently, like the Pantheon. Rome had a places for activities to keep people engaged like chariot races, musical and theatrical performances, public executions and gladiatorial combat. In the Colosseum, Rome’s amphitheatre, 60,000 persons could be accommodated.
The collection of Roman mosaics are some of the finest in the world that embellish the floors they depict hunting scenes and everyday life, and girl athletes (Bikini girls)
Herculaneum was a wealthier town than Pompeii, possessing an extraordinary density of fine houses.
The House of the Faun is an ancient, private house located in Pompeii. It was one of the largest and most richly decorated houses of the Roman republic period
Young woman, Fresco from Pompeii, c. 60 AD (often referred to as 'Sappho')
The four “Pompeian” styles of painted wall decoration which appear throughout Italy and the Roman world
Aristocratic women managed a large and complex household. with dozens or even hundreds of slaves,
Trier was one of the five biggest cities in the known world Trier was one of the residences of the Western Roman Emperors
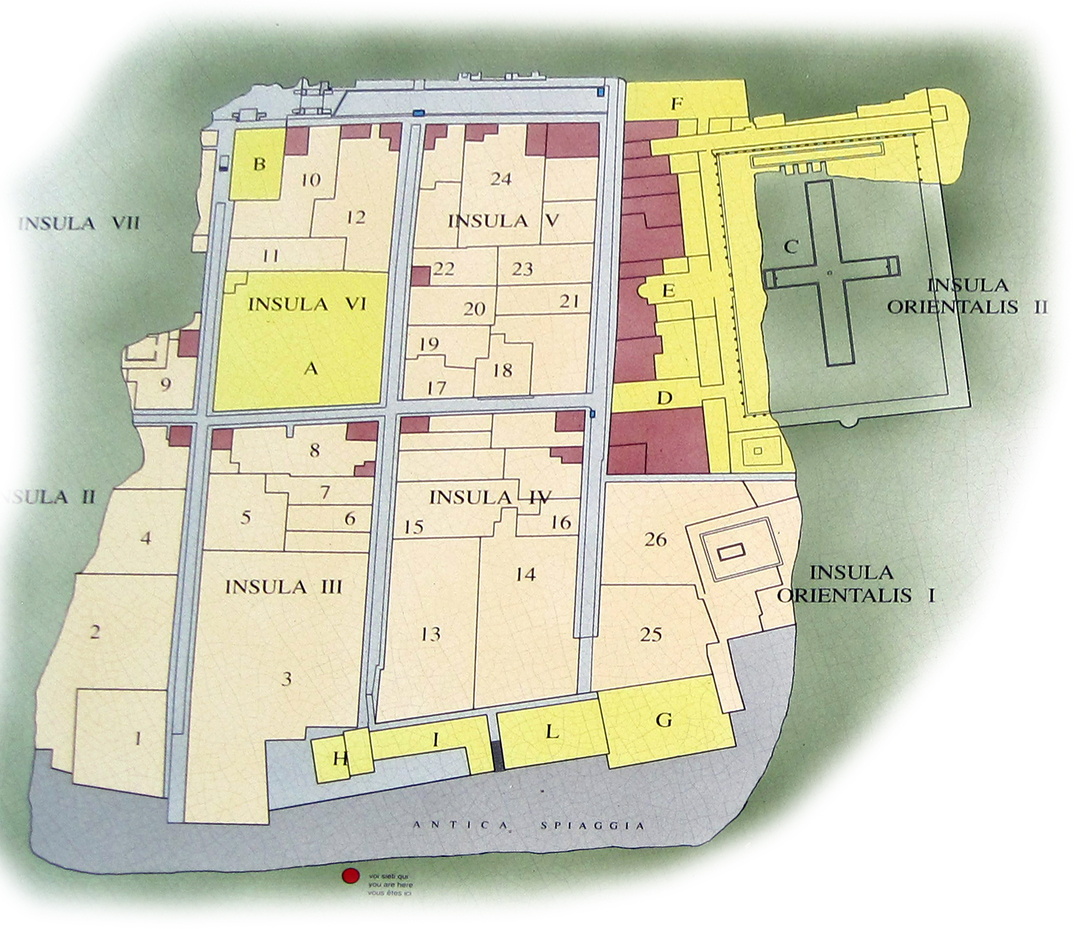
Ostia grew to 50,000 inhabitants in the 2nd century, reaching a peak of some 100,000 inhabitants in the 2nd and 3rd centuries
In founding a new city, one of the first things which the practical Romans provided was an abundant supply of water
Roman coinage, circulated throughout the provinces of the Empire, serving to familiarise the populaces with iemperors of whom they would never see in person.
Christians were first, and horribly, targeted for persecution as a group by the emperor Nero in 64 AD.
The fact that many ancient Roman monuments are still standing is evidence of how good Roman architecture really was